
Silica Glasses can Serve as Visible Luminescence Materials
Most recently, a research team led by Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has succeeded in strengthening photodarkening resistance of Dy3+ in silica glasses. The study was published in Journal of the American Ceramic Society. In their experiment, valence change of Dy ions and the formation of defects such as Al OHC from within the glass matrix caused by irradiation was inhibited by increasing the P/Al ratio.
Moreover, the introduction of P can form a valence equilibrium and stable [PAlO4] structure with Al, which suppresses the formation of Al related defects and thus improves the photodarkening resistance of Dy doped silica glasses.
This research may lead to a host material for fiber laser operated at visible wavelength.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
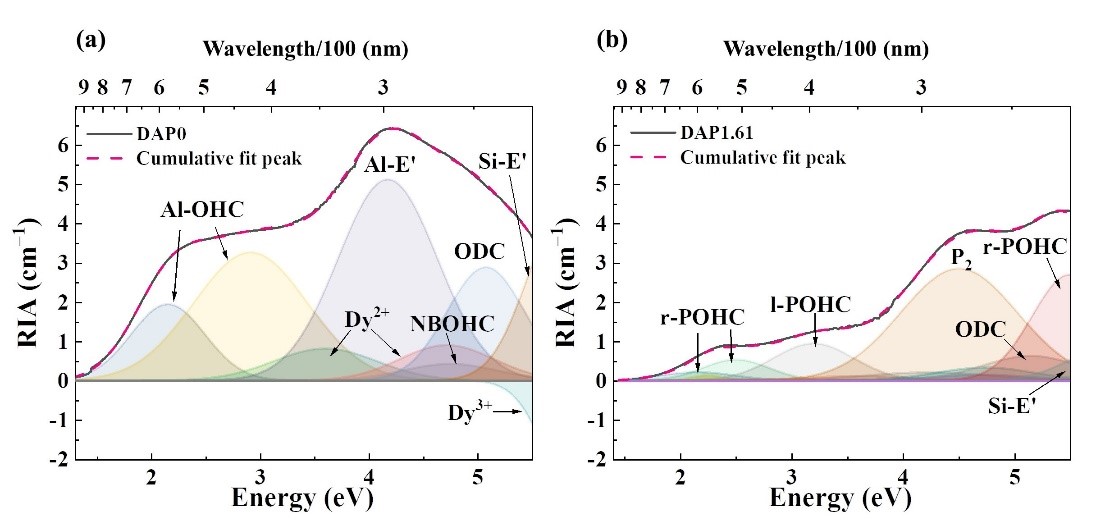
Characterizations of Dy3+ doped silica glasses.
Article website: